If you’re seeking information on CKS certification, CKS exam details, CKS syllabus, or CKS practice exams, you’ve come to the right place. Designed specifically for Kubernetes Security Experts, our guide is tailored to help you excel in the Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist (CKS) Exam.
In this comprehensive CKS Exam guide, you’ll find a thorough exploration of the CKS exam’s crucial components. Moreover, we’ll share invaluable tips and insights that played a pivotal role in achieving remarkable CKS exam results.
Looking to save on your CKS exam voucher? We’ve got you covered as well with information on cost-effective options for Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist certification exam fees. Let’s embark on this CKS certification journey together.
What is Kubernetes ?

Kubernetes, also referred to as “kube” or “k8s,” is software that automatically manages, scales, and maintains multi-container workloads in desired states.
Modern software is increasingly run as fleets of containers, sometimes called microservices. A complete application may comprise many containers, all needing to work together in specific ways. Kubernetes is software that turns a collection of physical or virtual hosts (servers) into a platform that:
- Hosts containerized workloads, providing them with compute, storage, and network resources, and
- Automatically manages large numbers of containerized applications — keeping them healthy and available by adapting to changes and challenges
Why use Kubernetes?
One of the benefits of Kubernetes is that it makes building and running complex applications much simpler. Here’s a handful of the many Kubernetes features:
- Standard services like local DNS and basic load-balancing that most applications need, and are easy to use.
- Standard behaviors (e.g., restart this container if it dies) that are easy to invoke, and do most of the work of keeping applications running, available, and performant.
- A standard set of abstract “objects” (called things like “pods,” “replicasets,” and “deployments”) that wrap around containers and make it easy to build configurations around collections of containers.
- A standard API that applications can call to easily enable more sophisticated behaviors, making it much easier to create applications that manage other applications.
The simple answer to “what is Kubernetes used for” is that it saves developers and operators a great deal of time and effort, and lets them focus on building features for their applications, instead of figuring out and implementing ways to keep their applications running well, at scale.
By keeping applications running despite challenges (e.g., failed servers, crashed containers, traffic spikes, etc.) Kubernetes also reduces business impacts, reduces the need for fire drills to bring broken applications back online, and protects against other liabilities, like the
What Is the Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist Exam?
The official CNCF certification page says :
The Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist (CKS) program provides assurance that a CKS has the skills, knowledge, and competence on a broad range of best practices for securing container-based applications and Kubernetes platforms during build, deployment, and runtime.
The CKS exam curriculum is thoughtfully organized, covering a wide range of topics that are directly relevant to Kubernetes security.
Why Kubernetes and CKS ?
If you’ve been considering taking the CKS (Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist) exam, it’s crucial to grasp the tremendous benefits it can bring to your career. Becoming a Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist demonstrates your expertise in securing Kubernetes clusters, making you a highly sought-after professional in the industry.
Since Kubernetes was open-sourced by Google in 2014, it has experienced an explosive surge in popularity, becoming a dominant force in the market. As a result, organizations are increasingly relying on Kubernetes for orchestrating containerized workloads and services, creating a soaring demand for skilled Kubernetes experts.
By obtaining the CKS certification, you position yourself at the forefront of this growing demand, making you an invaluable asset to any company that uses Kubernetes in production. A quick search on professional platforms like LinkedIn will reveal numerous job opportunities specifically seeking candidates with CKS credentials.
The CKS exam not only validates your skills in Kubernetes security but also proves your dedication to staying current with the latest technologies and industry best practices.
Employers recognize the value of certified professionals who can enhance the security posture of their Kubernetes deployments.
Furthermore, Kubernetes is the driving force behind modern infrastructure, and countless organizations are either adopting it or planning to do so in the near future. By becoming a CKS-certified expert, you position yourself as a pioneer in this dynamic and evolving field.
[20 % Off] Linux Foundation CKS Exam Voucher Code
Your first step toward CKS Exam is to register for the exam. You can appear for the exam anytime in 12 months with a free retake.
Register today and use our exclusive coupon code TECK20 for the CKAD exam to get a 20% discount on CKS (and KCNA, CKA, and CKAD certifications ). This code expires soon.
With CKS exam registration, you will get free access to killer.sh platform CKS practice exam simulator. Before appearing for the CKS exam, you can practice for the exam in the simulator.
You can access the simulator from the exam portal. You can directly log in with the Linux foundation credentials. You will have access to two exam sessions. In fact, the simulator exam is harder than the actual exam. So, if you try to get a passing mark on the simulator, you will definitely learn the actual CKS exam.
Note
Save $80 Today on CKA | CKAD | CKS certification using the Voucher code TECK20 .
Offer Ends Soon !
Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist (CKS) Exam Study Guide
In this section of CKS Exam Study Guide , we will provide an extensive list of CKS resources along with direct links to the official documentation. These resources will be instrumental in supporting you during the CKS exam by providing detailed information and guidance.
CKS Exam Prerequisites
If you aspire to become a Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist (CKS), it’s essential to meet certain requirements to ensure a smooth certification journey. Prior to attempting the CKS exam, candidates must have successfully taken and passed the Certified Kubernetes Administrator (CKA) exam.
While there are no official prerequisites beyond the CKA certification, it’s vital to possess a strong understanding of Kubernetes fundamentals. If you’re new to Kubernetes and unsure about its concepts, we highly recommend familiarizing yourself with the basics before scheduling your exam.
Please refer to our CKA Exam Study Guide here :
CKS Exam Details
| Exam Duration | 2 hrs |
| Pass Percentage | 67% |
| Exam Format | Online proctored |
| Number of questions | 15-20 performance-based tasks |
| Prerequisite | CKA Certification |
| Results | 24 Hours |
| Retry policy | 2 Attempts |
| Kubernetes Version ( since 05/2023) | v1.28 |
| CKS Validity | 2 Years |
| CKS Certification Exam Cost | $395 |
Linux Foundation CKS Exam Syllabus
This is the most important part of CKS Exam Study Guide , the curriculum for the exam:
| Topic | Concepts | Weightage |
|---|---|---|
| Cluster Setup | 1. Use Network security policies to restrict cluster level access 2. Use CIS benchmark to review the security configuration of Kubernetes components (etcd, kubelet, kubedns, kubeapi) 3. Properly set up Ingress objects with security control 4. Protect node metadata and endpoints 5. Minimize use of, and access to, GUI elements 6. Verify platform binaries before deploying | 10 % |
| Cluster Hardening | 1. Restrict access to Kubernetes API 2. Use Role Based Access Controls to minimize exposure 3. Exercise caution in using service accounts e.g. disable defaults, minimize permissions on newly created ones 4. Update Kubernetes frequently | 15% |
| System Hardening | 1. Minimize host OS footprint (reduce attack surface) 2. Minimize IAM roles 3. Minimize external access to the network 4. Appropriately use kernel hardening tools such as 5. AppArmor, seccomp | 15% |
| Minimize Microservice Vulnerabilities | 1. Setup appropriate OS level security domains 2. Manage kubernetes secrets 3. Use container runtime sandboxes in multi-tenant environments (e.g. gvisor, kata containers) 4. Implement pod to pod encryption by use of mTLS | 20% |
| Supply Chain Security | 1. Minimize base image footprint 2. Secure your supply chain: whitelist allowed image registries, sign and validate images 3. Use static analysis of user workloads (e.g. kubernetes resources, docker files) 4. Scan images for known vulnerabilities | 20% |
| Monitoring, Logging, and Runtime Security | 1. Perform behavioral analytics of syscall process and file activities at the host and container level to detect malicious activities 2. Detect threats within physical infrastructure, apps, networks, data, users and workloads 3. Detect all phases of attack regardless where it occurs and how it spreads 4. Perform deep analytical investigation and identification of bad actors within environment 5. Ensure immutability of containers at runtime 6. Use Audit Logs to monitor access | 20% |
Unlocking the CKS exam’s domain-wise syllabus can be a bit challenging, as determining the chapters that fall under each domain requires careful consideration.
Please refer to my post about the CKS Curriculum 1.28 to get an expertly curated, detailed list of syllabus topics, making this task much more manageable.
CKS Exam Format
Prepare for an engaging and practical experience during the CKS exam, where you’ll be presented with hands-on problem-solving scenarios to tackle within a 120-minute timeframe.
This performance-based exam stands apart from traditional multiple-choice formats, focusing on your ability to solve real-world challenges in a command line environment. Expect to encounter a set of performance-based problems that will put your Kubernetes skills to the test.
CKS Exam Interface
According to official Linux Foundation documentation :
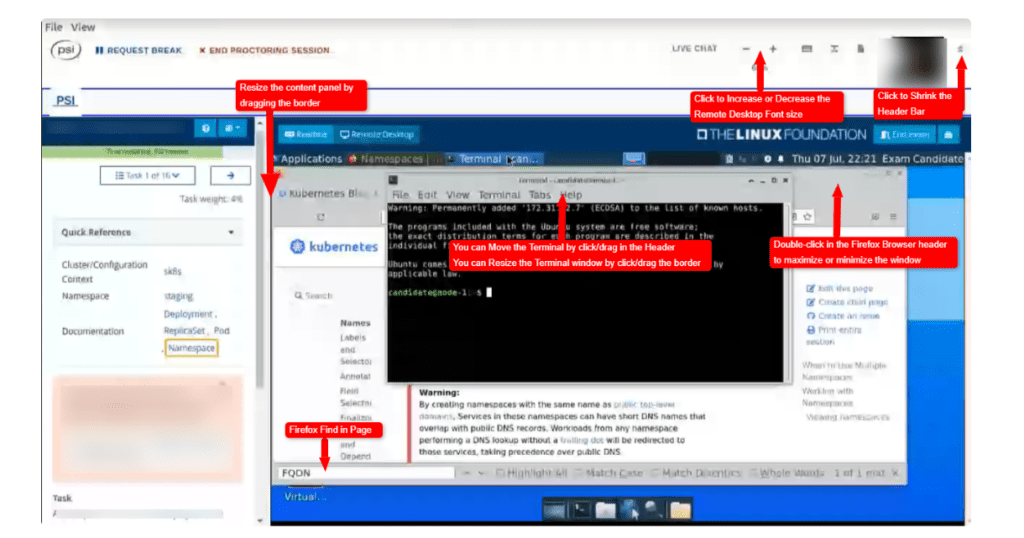
As of June 2022, there is a change in the exam platform. It is just an exam platform, so the exam questions will not change, but there were a few things that seemed to concern you, so I will write them down.
| Each task in this exam must be completed in a specific cluster/configuration context. The exam environment consists of sixteen clusters, one for each task. Each cluster consists of a master node and a worker node. |
You can switch the cluster/configuration context with a command like the following:kubectl config use-context <cluster/context name> |
| For displays, do note that previously, we were allowed to use more than 1 display. However, this is no longer the case. Only 1 active display is only allowed when you take the exam |
| You can browse the official documentation for reference, you can do that within the remote desktop environment as well as it has Firefox browser pre-installed |
CKS Exam Environment
Sixteen clusters comprise the exam environment, one for each task. Each cluster is made up of one master node and one worker node.
- An infobox at the start of each task provides you with the cluster name/context and the hostname of the master and worker node.
- You can switch the cluster/configuration context using a command such as the following:
kubectl config use-context <cluster/context name> - Nodes making up each cluster can be reached via ssh, using a command such as the following:
ssh <nodename> - You have elevated privileges on any node by default, so there is no need to assume elevated privileges.
- You must return to the base node (hostname cli) after completing each task.
- Nested
−sshis not supported.
CKS Exam Preparation Resources
In the following discussion of CKS Exam Study Guide, I will cover official Kubernetes resources that are invaluable for preparing for each topic of the CKS exam. These documentation pages can serve as a valuable reference during the exam preparation.
CKS Exam Allowed Resources
The CKS exam is an open-book exam. You have access to the resources:
- In certain questions, you’ll find YAML templates available for your use. Feel free to leverage these templates and modify the variable values as required to match the given instructions.
- During the exam, make sure to utilize the browser within the VM to access the Kubernetes Official Documentation, which is a valuable resource at your disposal.
- You can access the Kubernetes Official Documentation and its subdomains at the following URLs:
- Main documentation: https://kubernetes.io/docs/
- Blog and subdomains: https://kubernetes.io/blog/
- Tools :
- Trivy documentation https://aquasecurity.github.io/trivy/
- Falco documentation https://falco.org/docs/
- AppArmor : https://gitlab.com/apparmor/apparmor/-/wikis/Documentation
- You can access the Kubernetes Official Documentation and its subdomains at the following URLs:
Read Important instructions and LF documentation
The information given by the Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF) and the Linux Foundation (LF) is very good and is something that you should familiarise yourself with.
More information about the exam can be found on the Linux Foundation official website
| Instructions about Exam | https://docs.linuxfoundation.org/tc-docs/certification/important-instructions-cks |
| Candidate Handbook | https://docs.linuxfoundation.org/tc-docs/certification/lf-handbook2 |
| System check | https://syscheck.bridge.psiexams.com/ |
CKS Exam Preparation Course
If you want to enroll in a course to prepare for the CKS, this one is all what you need :

I highly recommend the course “Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist” on Udemy. This comprehensive course covers a wide range of topics essential for securing Kubernetes environments.
You’ll learn about Kubernetes architecture, secure networking, access controls, authentication and authorization, container security, auditing, and much more. With practical exercises and a knowledgeable instructor, this course prepares you to tackle the security challenges associated with Kubernetes deployments effectively. Enroll now to gain the expertise needed to protect your Kubernetes clusters.
Github CKS Course and commands
I highly recommend the “Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist (CKS) Course” available on GitHub by kodekloudhub. This course provides comprehensive materials and resources to prepare for the CKS exam. It covers a wide range of topics related to Kubernetes security, including securing cluster components, container security, network policies, RBAC, and more. The course offers hands-on labs and exercises to enhance your practical skills. It is an excellent resource for anyone seeking to gain expertise in securing Kubernetes clusters.
CKS Exam Practise Labs and Mock Exams
- Mock Exams : Killer.sh ( 2 sessions)
Aspiring Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist (CKS) can now take advantage of an exam simulator provided by Killer.sh. Upon registering for the CKS exam, candidates are eligible for two attempts, each of which offers 36 hours of access, starting from the activation moment. These simulations comprise of 20-25 questions that closely resemble the types of questions that may appear on the actual CKS exam.
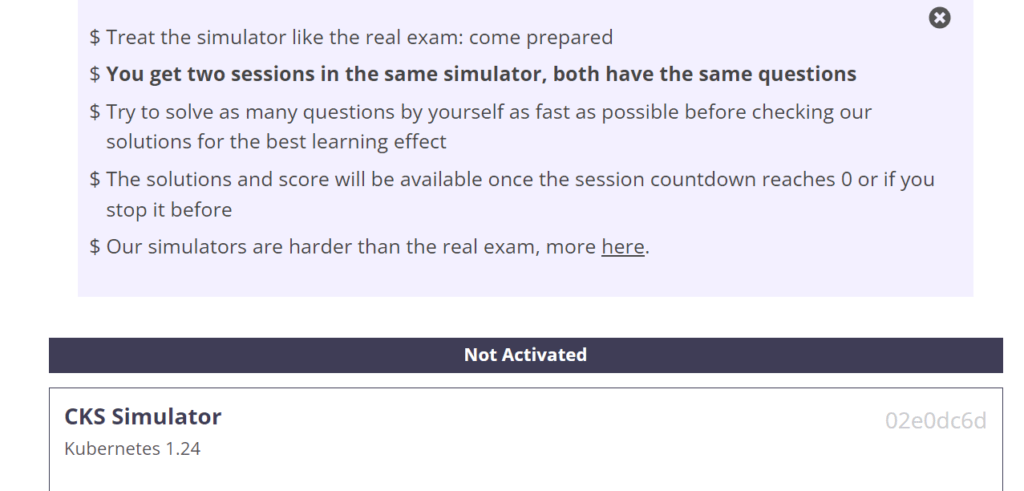
MY advice : Aim to achieve a Killer Shell score of at least 90% before sitting the CKS EXAM
The Killercode CKS Playground is a simulation tool for individuals preparing for the Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist (CKS) exam. It provides a realistic testing environment for candidates to practice their knowledge and skills in securing Kubernetes clusters. The simulation contains questions similar to what can be expected on the actual exam, allowing candidates to get a feel for the format and level of difficulty.
This part of Kubernetes documentation offers the possibility to play with preconfigured k8s clusters

Useful CKS EXAM Bookmarks
- kubectl Cheat Sheet — https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/kubectl/cheatsheet/
- Kubectl Commands — https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/generated/kubectl/kubectl-commands
- Network Policies — https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/network-policies/
- Security Context — https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/security-context/
- Secrets — https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/secret/
- RBAC — https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/access-authn-authz/rbac/
- Seccomp — https://kubernetes.io/docs/tutorials/clusters/seccomp/
- Apparmor — https://kubernetes.io/docs/tutorials/clusters/apparmor/
- ImageWebhookPolicy — https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/access-authn-authz/admission-controllers/
- Audit Policy — https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/debug-application-cluster/audit/
- PodSecurityPolicy — https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/policy/pod-security-policy/
- Kubelet Config — https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/config-api/kubelet-config.v1beta1/
- RuntimeClass — https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/containers/runtime-class/
- Admission Controllers — https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/access-authn-authz/admission-controllers/#podsecuritypolicy
- automountServiceAccountToken — https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/configure-service-account/
- Pod Volumes — https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/storage/volumes/
- PV PVC — https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/configure-persistent-volume-storage/
- Ingress — https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/ingress/
Top 5 Tips for CKS Exam in 2023
For this CKS Exam Study Guide readers , Here are some quirky but professional tips to ace the CKS Kubernetes Exam in 2023:
Practice , Practice , Practice …
This exam is hands-on in nature, emphasizing the importance of proficiency with the Kubernetes command line interface (kubectl).
It is essential to cultivate a high level of comfort and familiarity with kubectl, practicing the art of typing commands swiftly and accurately.
As mentioned earlier, please ensure that you review the practice exam provided in Mumshad Mannambeth’s Udemy course. It is highly recommended to enroll in the two killer,sh, hands-on sessions and aim for outstanding scores in order to thoroughly prepare yourself before attempting the actual exam.
Time management
Since you will be executing the kubectl command multiple times, setting up aliases can save you valuable seconds with each entry. For instance, assigning an alias like ‘k’ for ‘kube-control’ can potentially grant you an additional minute or two towards the end of the exam
alias k=kubectl
If you encounter a question or problem that is unfamiliar to you during the CKS exam, don’t fret. Instead, opt to skip it temporarily and revisit it later. Utilize the notepad as a tracking pad, jotting down all the questions you skipped along with their respective weights.
For instance, if you skip two questions with weights of 8% and 2%, prioritize revisiting the question with the higher weight first. This approach ensures that you maximize your potential score by focusing on questions with greater significance.
Review Completed Tasks
After each question, it is crucial to review your work meticulously to ensure accuracy. Avoid the risk of spending 10-15 minutes on a question and unintentionally overlooking potential errors
For example, if you have created a pod , it is highly recommended to check its status before moving on to another task. This verification step ensures that the pod is created and started.
kubelet get pod <podName>
Stress Management
No Need to Panic! Here’s Why:
If it’s your first attempt at the exam, remember that you have additional chances to try again if needed. There’s no need to feel overwhelmed.
Moreover, the good news is that you only require a passing score of 67% to crack the exam successfully. So, stay focused, do your best, and approach the test with confidence. You’ve got this!
Configuration Management during the Exam
As mentioned previously, the CKA exam environment consists of six clusters, each with its own dedicated set of nodes. Carefully change context while attempting questions.
At the start of each task you’ll be provided with the command to ensure you are on the correct cluster to complete the task , for example :
kubectl config use-context k8sAn example of command to ssh to a master node :
ssh mk8s-master-0 Us elevated privileges on the master node :
sudo -iDuring the exam, when you need to make modifications to certain files, always take a backup of those files before proceeding with any changes. This precaution ensures that if anything goes awry or if something isn’t functioning as expected, you can easily restore the original file and start fresh.
Additionally, a great advantage in the CKS Exam is that for some questions, you’ll find example manifests of the tasks you need to perform. These example files are conveniently stored at specific locations. This feature saves you valuable time, as you won’t need to manually copy from documentation and then make modifications.
Top 5 CKS Exam DON’T’s
- Take your time; don’t rush into the terminal. Read the question twice before proceeding.
- Avoid writing YAML files from scratch when possible.
- Use aliases wisely; don’t overwhelm yourself with too many.
- Stay calm if you get stuck; flag the question and move forward. You can return to it later. Each question carries a weightage, so prioritize accordingly.
- Avoid scheduling the exam on the last day to allow time for potential retakes.
CKS Exam Sample Question
CKS EXAM QUESTION
# Enable Audit logs for the Kubernetes API server of your cluster.
# There is an existing configuration file stored in your master node at /etc/kubernetes/audit/policy.yaml.
# Add a policy to the configuration so that audit logs contain metadata for all resources. Additionally, it should log the request body for configmap resources.
# Change the configuration of the Kube API Server to enable audit logging using the policy configuration created above. Write logs to the path /var/log/audit/audit.log.CKS Exam Sample Solution
# The first part of the task is to configure the audit policy so that audit logs will contain metadata of all requests and request body of requests to config. We can accomplish this using this policy configuration:
###### STEP 1 : Kubernetes audit log configuration file ######
# /etc/kubernetes/audit/policy.yaml
# Log all requests at the Metadata level.
apiVersion: audit.k8s.io/v1
kind: Policy
rules:
- level: Metadata
# Log configmap and secret changes in all other namespaces at the Metadata level.
- level: Request
resources:
- group: ""
resources: ["configmaps"]
###### STEP 2 : Configure Kube API server for audit logs ######
#The second step of the task is to configure the Pod for the Kubernetes API server. You can change the API server’s configuration by editing its manifest. Usually, it is stored at /etc/kubernetes/manifests/kube-api-server.yaml on the master nodes.
#We need to:
# + Configure the log path
# +Configure the path to the audit policy configuration file
# +Mount the audit policy to the Kube API server
# +Mount the logs directory
# First, add the following additional arguments:
--audit-policy-file=/etc/kubernetes/audit/policy.yaml
--audit-log-path=/var/log/audit/audit.log
# Then add volumes to the pod description:
volumes:
- hostPath:
path: /var/log/audit
type: DirectoryOrCreate
name: audit-logs
- hostPath:
path: /etc/kubernetes/audit/policy.yaml
type: File
# Next, add the volumeMounts and apply the new configuration:
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /var/log/audit
name: audit-logs
readOnly: false
- mountPath: /etc/kubernetes/audit/policy.yaml
name: audit-policy
readonly: true
# Congrats, you activated the audit logs for your Kubernetes API Server.
# You can check that logs are written by running the following on your node:
cat /var/log/audit/audit.log
Example of scripts and commands
- Retrieve and decode an existant kubernetes secret :
k get secret cks-secret1 -n teckbootcamps-dev
k get secret cks-secret1 -n teckbootcamps-dev -o json
k get secret cks-secret1 -n teckbootcamps-dev -o jsonpath='{.data.client-id}' | base64 --decode
k get secret cks-secret1 -n teckbootcamps-dev -o jsonpath='{.data.client-secret}' | base64 --decode 
- Create a pod and attach a secret to it as a volume :
kubectl create secret generic cks-exam-secret2 -n teckbootcamps-dev \
--from-literal=client-id=cks-username2 \
--from-literal=client-secret='Secret2022:)'
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: teckbootcamps-pod
namespace: teckbootcamps-dev
spec:
containers:
- name: teckbootcamps-container
image: nginx
volumeMounts:
- name: my-secret-volume
mountPath: "/etc/secret/2022"
readOnly: true
volumes:
- name: my-secret-volume
secret:
secretName: cks-exam-secret2
k exec teckbootcamps-pod -n teckbootcamps-dev -- cat /etc/secret/2022/client-id
k exec teckbootcamps-pod -n teckbootcamps-dev -- cat /etc/secret/2022/client-secret
Conclusion
In this post, I went over the essential steps you need to take to prepare for the CKS exam, including registering for the exam, reading important instructions and LF documentation, taking CKS certification courses, practicing with CKS practice labs and exams, and managing stress and time during the exam.
I also provided tips and notes for the CKS exam, including the importance of practicing, time management, and configuration management. Additionally, I included an outline of the exam syllabus, exam interface, and example scripts and commands.
Remember, with dedication, hard work, and the right resources, you too can become a Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist!